Cannabis or Hemp?
Plants ranging from huge fiber-producing industrial hemp plants to the most potent of medicinal strains. These terms are interchangeable.
Cannabis
The name given to the plant itself. A total of 480 natural components have been found within the cannabis plant. There are three major types of cannabis (plus multiple hybrids), distinguished by very different characteristics and traits they display:
- Cannabis sativa
- Cannabis indica
- Cannabis ruderalis
Hemp–(Industrial Hemp)
Industrial hemp is cannabis with a THC content of less than 0.3%.
Marijuana
Classified as a psychoactive cannabis, meaning it is rich in THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol).Contrary to what many pot smokers may tell you, marijuana is addictive. Even among occasional users, one in 12 can feel withdrawal symptoms if they can’t get high when they want to. Many experts also believe marijuana is physically addictive.
Medical Cannabis/Medical Marijuana
Cannabis used as a physician-recommended form of medicine or herbal therapy typically higher in THC content – (higher than 0.3%) than other species of cannabis.
Tetrahydrocannabinol-THC
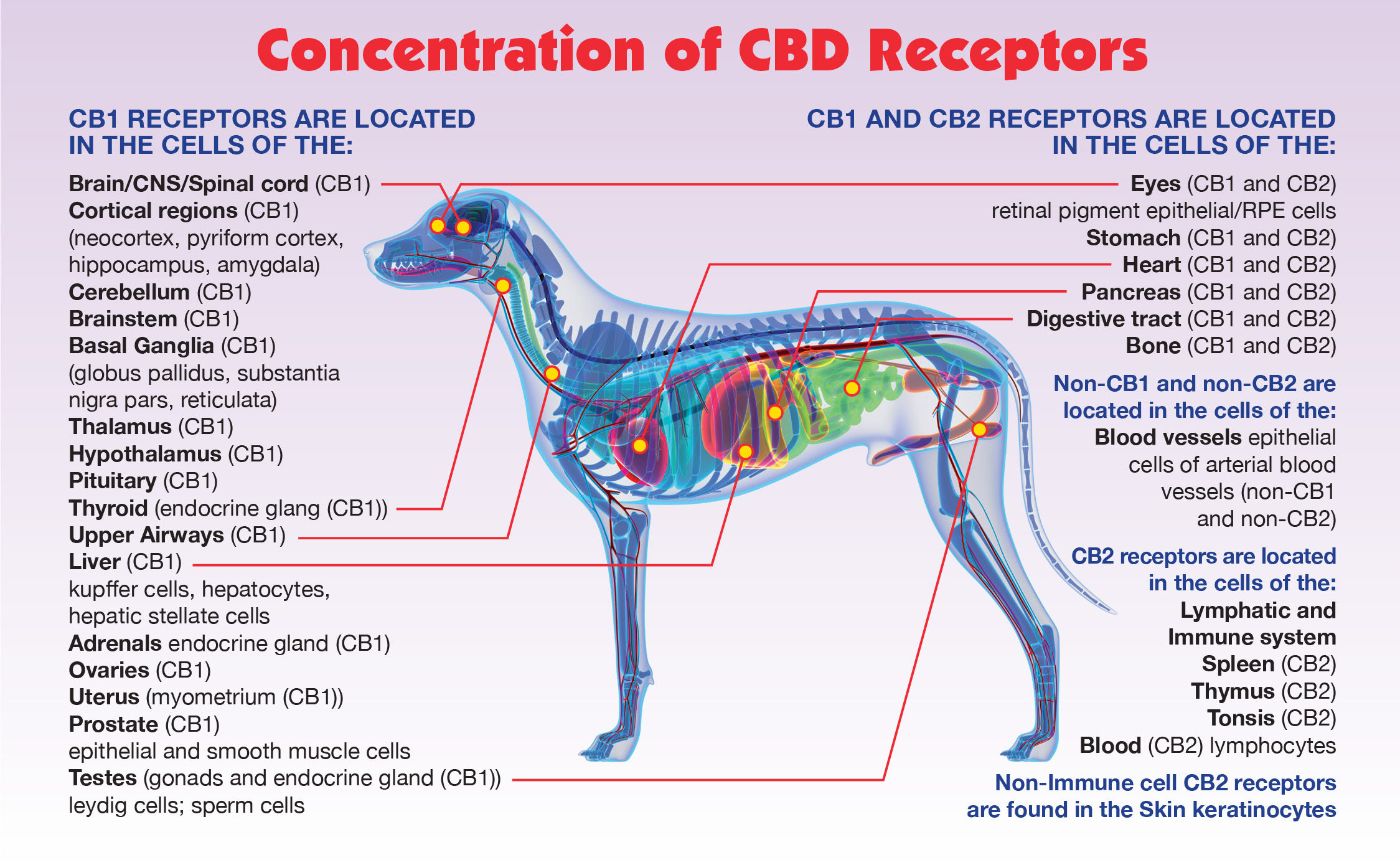
delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol. This is a schedule I controlled substance. The only thus far identified psychoactive component of cannabis (the cannabinoid that makes people high) reacting with CB-1 receptors that are generally concentrated in the brain and central nervous system, and CB-2 receptors that are generally concentrated in peripheral organs and cells associated with the immune system.
Cannabidiol-CBD
A naturally occurring constituent/cannabinoid of the hemp plant. It is the most abundant, non-psychoactive cannabinoid in hemp/cannabis, and reacts primarily with CB-2 receptors that are generally concentrated in peripheral organs and cells associated with the immune system.
CBD has been scientifically shown to: (relieve pain, stimulate appetite, reduce vomiting & nausea, reduce contractions in small intestines, relieve anxiety, reduce seizures, suppress muscle spasms, reduce blood sugar levels, reduce nervous system degeneration, kill or slow bacterial growth, inhibit cell growth in tumors/cancer cells, and promote bone growth).
It is absorbed by the digestive tract, enters the hepatic portal system through the portal vein and on to the liver before being shipped off to other locals, and is eliminated in feces, urine, sweat, oral fluid, and hair.